The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is part of the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP). It allows security researchers to quantitatively evaluate the risk posed by a vulnerability. CVSS is comprised of three metric groups. The scoring ranges from 0-10. For the purposes of the current version of the exam (as of 1/1/2019), CVSS v2 is used.
- 0: No Issues
- 0.1 to 3.9: Low
- 4.0 to 6.9: Medium
- 7.0 to 8.9: High
- 9.0 to 10.0: Critical
Base Metric
Access Vector (AV): This how a vulnerability can be exploited.
- Local (L): The attacker must have physical or logical access directly to the system.
- Adjacent (A): The attacker must be on the local network.
- Network (N): The attacker can exploit the vulnerability from any network.
Access Complexity (AC): This metric describes the difficulty of exploiting the vulnerability.
- High (H): The vulnerability requires special conditions that are not easily met.
- Medium (M): The vulnerability requires special conditions that are somewhat difficult to meet.
- Low (L): The vulnerability doesn’t require any special conditions to exploit.
Authentication (Au): This metric describes how much authentication the attacker needs to exploit the vulnerability.
- Multiple (M): Two or more authentication mechanisms must be completed to exploit the vulnerability.
- Single (S): A single authentication mechanism must be completed to exploit the vulnerability.
- None (N): No authentication is necessary to exploit the vulnerability.
Confidentiality (C): The level of information disclosure that could occur.
- None (N): No information disclosure.
- Partial (P): Some access to the information.
- Complete (C): All information could be compromised.
Integrity (I): What type of alteration of data may occur.
- None (N): No data integrity changes.
- Partial (P): Some data integrity may be affected.
- Complete (C): All data could be compromised.
Availability (A): Describes the impact on system availability that may occur.
- None (N): No impact on
availability of the system. - Partial (P): Some impact on
availability of the system. - Complete (C): Complete shutdown of the system.
The combination of the basic metrics is called the CVSS vector. An example vector is CVSS2#AV:L/AC:H/Au:N/C:P/I:P/A:N. NIST provides a calculator that will allow for the various basic metrics to be chosen and a CVSS score generated. The calculator also allows the calculation of Temporal and Environmental metrics.



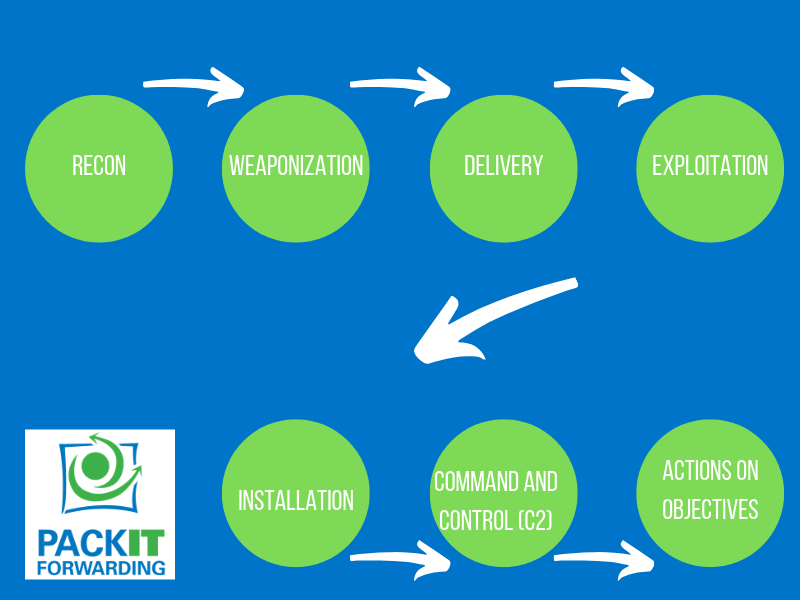

bullshit
Would you care to provide a constructive dialogue?